|
|
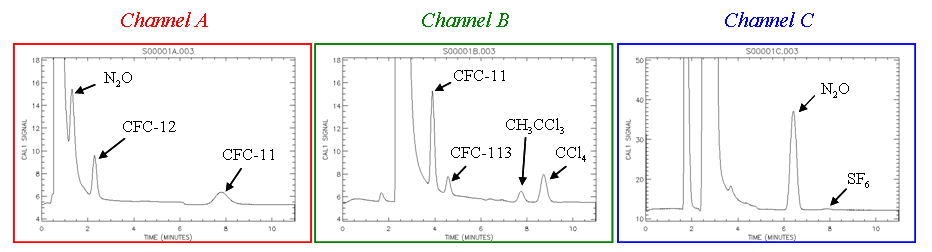
Figure 1. Chromatograms from each of the three RITS channels. These plots are all from the same calibration sample injection -- the first sample injection of the new millenium (GMT) at CMDL's Samoa observatory. |
RITS System DescriptionA RITS system in its fullest form consisted of 2 GCs and 3 separation columns
(channels), each loaded with a unique packing material for the measurement of
N2O, CFC-12, CFC-11, CH3CCl3, and CCl4, with
dual-channel redundancy for N2O and CFC-11. N2 was the carrier
gas used on the chlorocarbon solvent (B) channel, while the two N2O channels
(A and C) used a 5% mixture of CH4 in Argon (called "P5") as the carrier gas.
The RITS system is summarized by channel in |
| RITS Channel |
Gas Chromatograph |
Carrier Gas |
Column Packing Material |
Detector | Measureable Compounds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Hewlett-Packard 5890 | P5 | Porasil B | Electron Capture |
N2O, CFC-12, CFC-11 |
| B | Hewlett-Packard 5890 | N2 | OV-101 | Electron Capture |
CFC-11, CFC-113, CH3CCl3, CCl4 |
| C | Shimadzu | P5 | Porapak Q | Electron Capture |
N2O, SF6 |

|
|
Figure 1. Chromatograms from each of the three RITS channels. These plots are all from the same calibration sample injection -- the first sample injection of the new millenium (GMT) at CMDL's Samoa observatory. |
|
|