More than two years after road access and electrical power to the Mauna Loa Observatory was cut off by lava flows, NOAA staff continue to make critical measurements of the atmosphere and other environmental variables at the remote site.
In 2023, observatory staff installed solar panels at the site and resumed some measurements, including the independent carbon dioxide monitoring programs run by the Global Monitoring Laboratory and Scripps Institution of Oceanography, as well as other atmospheric measurements.
Construction of a temporary road to access the observatory site is anticipated to begin in summer 2025.
Media can contact: Theo Stein (303) 819-7409 (theo.stein@noaa.gov)
News

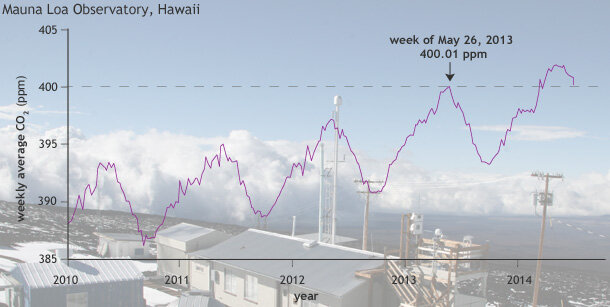
2013 State of the Climate: Carbon dioxide tops 400 ppm
On May 9, 2013, the daily average concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere surpassed 400 parts per million (ppm) for the first time at the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii, where the modern record of observations began back in 1958. Other Northern Hemisphere sites also reported CO2 concentrations exceeding 400 ppm in 2013. By summer, the high concentrations at these sites had dropped as vegetation began taking up carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.